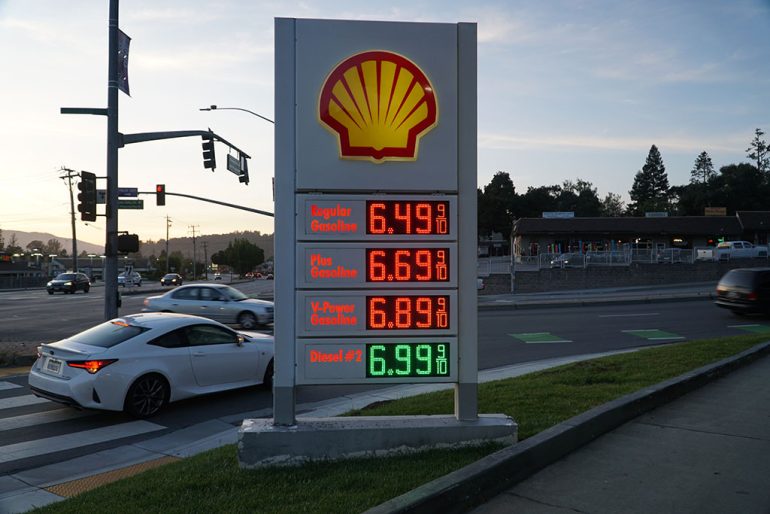
In a pivotal decision, California’s air regulators have approved updates to the state’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS), aiming to push the needle further on climate action. However, the California Air Resources Board’s (CARB) new rules could come at a cost to residents at the pump, with analysts suggesting gas prices may rise significantly in the coming years.
The LCFS, initially adopted in 2009, is California’s pioneering policy designed to lower the carbon intensity of transportation fuels. By setting stringent emissions reduction targets, the LCFS incentivizes producers to reduce the environmental impact of gasoline and other transportation fuels. This latest set of revisions, approved after a lengthy public meeting, raises the program’s targets even further. It also allocates funding for the expansion of zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) charging stations across the state, laying the groundwork for a cleaner transportation infrastructure.
Also, don’t forget that you can get discounted new car pricing with a free quote through qualified local dealer partners.
One notable shift is the plan to phase out subsidies for capturing methane emissions from dairy farms, which has been a contentious point. Previously, methane capture was rewarded for its climate benefits as the captured methane could be repurposed as a biofuel. Critics argue that this approach favored biofuel production when California should focus more exclusively on direct support for electric vehicles and infrastructure.
California’s updated LCFS proposal has attracted a range of criticisms from environmentalists, economists, and the oil industry. Environmental groups like Earthjustice contend that the LCFS has diverted too much focus toward biofuels instead of fully committing to zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) support. Adrian Martinez from Earthjustice called the program “a bridge for combustion fuels” that may now need re-evaluation, given the federal political landscape and the recent election of former President Donald Trump to a second term.
At the same time, state lawmakers and analysts are wary of potential gas price increases. Climate economist Danny Cullenward estimated that the LCFS updates could lead to gas prices rising by as much as $1.50 per gallon by 2035, although CARB has cautioned against making direct predictions due to economic uncertainties. For communities already struggling with high living costs, the potential impact at the pump raises concern. State Assemblymember Tom Lackey, a Republican representing the 34th District, argued that California’s residents, particularly those in lower-income areas, cannot afford such a steep increase in fuel prices.
According to CARB’s leadership, the long-term benefits of the LCFS program will outweigh any near-term costs. Steven Cliff, CARB’s executive officer, noted that the LCFS has already made lower-cost, low-carbon alternatives more accessible in California, positioning the state as a leader in sustainable fuel innovation. By funding ZEV infrastructure, the board hopes to accelerate California’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2045.
Supporters of the LCFS, such as EV Realty’s chief commercial officer, Suncheth Bhat, see the program as crucial for transitioning to a clean-energy future. “The LCFS is one of the most powerful, transformational policies we have to speed up the transition to electric vehicles,” Bhat said, highlighting the critical role of government-led climate policy in creating systemic change.
With former President Trump returning to office, California’s unique climate policies may again face federal pushback. Trump’s administration famously revoked California’s ability to set its own tailpipe emissions standards in 2019, a power that was later restored by President Biden and upheld in court. The state’s ability to maintain independent climate regulations could be challenged again, potentially hindering California’s progress on emissions reduction and vehicle electrification.
This political uncertainty only adds to the pressure on California’s regulators. CARB hopes the LCFS will bridge the gap until California achieves full electrification, but experts like David Pettit from the Center for Biological Diversity argue that a stronger focus on electric vehicles is needed, especially in light of possible regulatory battles with federal agencies.
California’s updated LCFS policy represents a bold step forward in the state’s quest for a cleaner future. But the complexities of energy economics, combined with the social and political ramifications of rising fuel costs, mean that CARB’s decision could lead to more than just environmental change.
As California heads toward its carbon-neutral goals, the debate over biofuels, gas prices, and EV incentives will likely intensify. Balancing these factors will be essential if California is to lead on climate change while keeping fuel costs manageable for its residents. Whether the updated LCFS ultimately succeeds in bringing cleaner, more affordable fuel options to Californians remains to be seen—but for now, the state’s approach will undoubtedly serve as a test case for climate policy nationwide.
Source: Associated Press